- Connect the FLS (fuel level sensor) to GNSS Tracker through the RS-232/RS-485 interface (via LLS protocol);
- Perform the FLS calibration in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions;
- Connect power from the on-board network to the GNSS Tracker;
- Configure the device and the cloud monitoring service (WIALON or any other, including your own);
- Now you can receive and process more accurate fuel level data on a cloud server than can be obtained from the CAN bus, keep more accurate statistics on fuel consumption and derive patterns, respond in time to cases of fuel theft.
Monitoring of truck placement and an enhanced fuel control
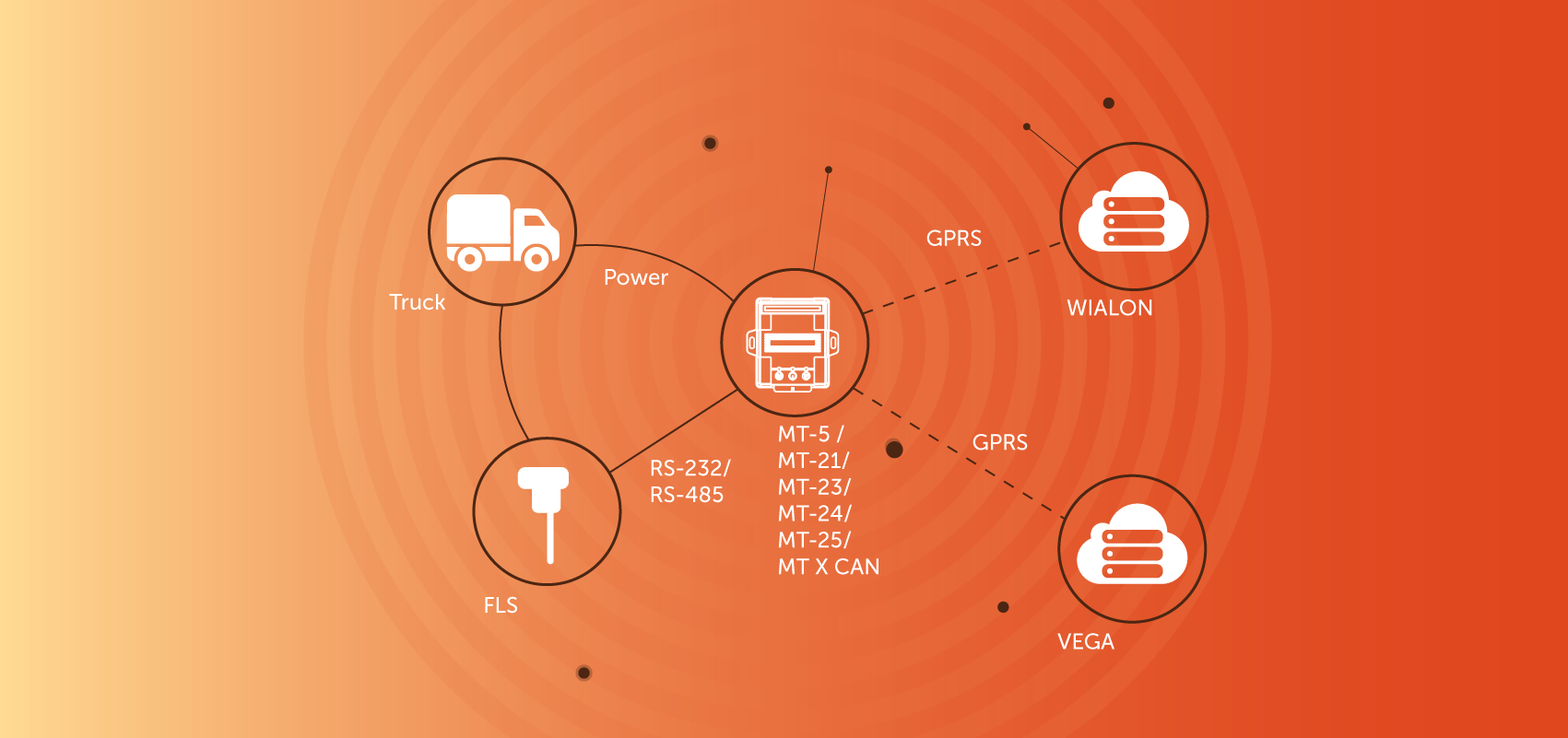
To implement the solution, you will need any of the devices with RS-232 or RS-485 interface. The devices have difference in additional functions, for example, the MT-25 device has voice support, and in the devices of the MT X CAN series a CAN-bus scanner is implemented to conveniently search for the necessary parameters for monitoring. When you have decided on the device, you must perform the following steps:
 Vega MT-5
Vega MT-5 Vega MT X Int
Vega MT X Int Vega MT X Ext
Vega MT X Ext Vega MT X LTE
Vega MT X LTE Vega MT-21
Vega MT-21 Vega MT-25
Vega MT-25 Vega M100
Vega M100 Vega M110
Vega M110 Vega M50
Vega M50 Vega M410
Vega M410 Vega MX600L
Vega MX600L Vega MX500
Vega MX500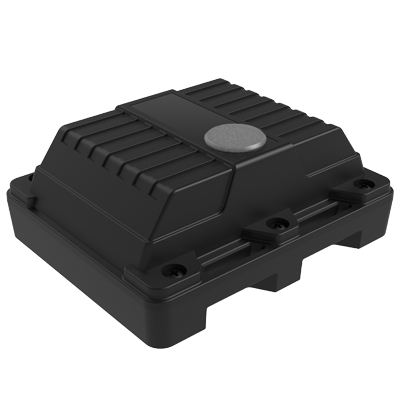 Vega MX810
Vega MX810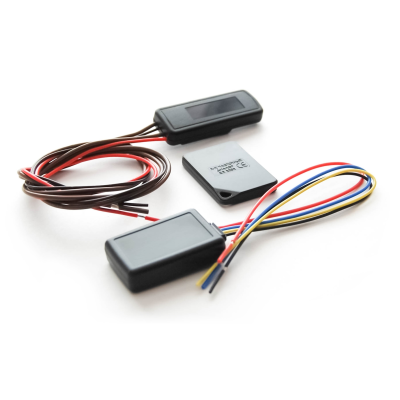 Vega RK-2.4
Vega RK-2.4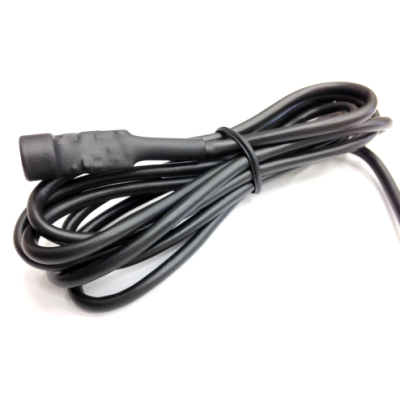 Vega SM-1
Vega SM-1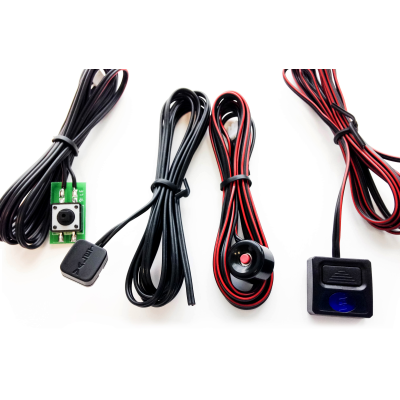 Buttons
Buttons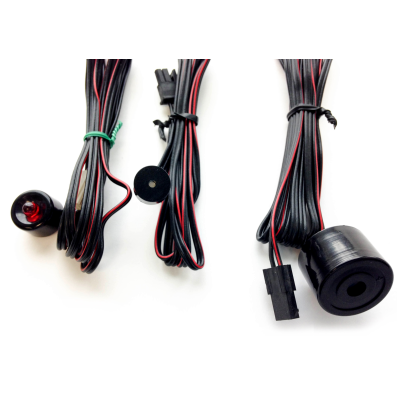 Indicators
Indicators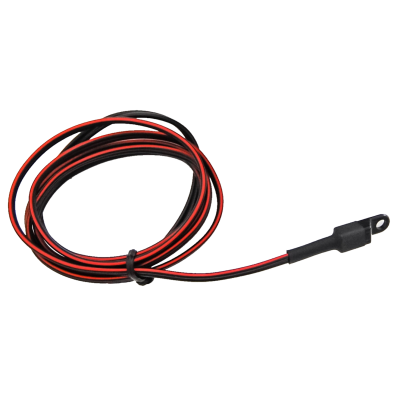 Vega ST-1
Vega ST-1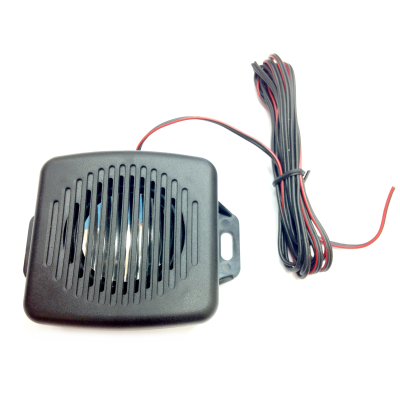 Vega SD-1
Vega SD-1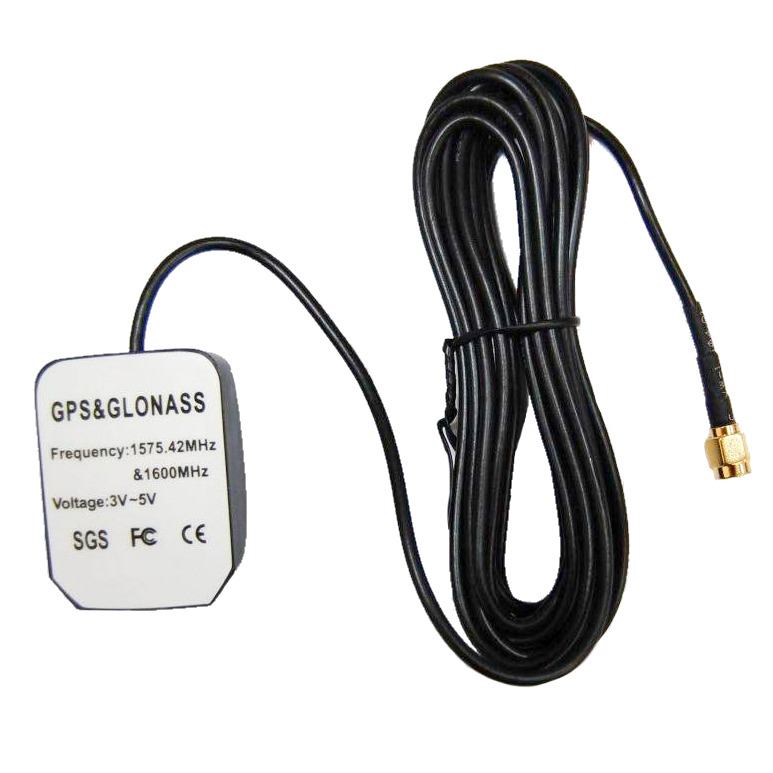 GLONASS/GPS Antennas
GLONASS/GPS Antennas GSM Antennas
GSM Antennas Connectors with Wires
Connectors with Wires Vega K-232
Vega K-232 Vega SA-1
Vega SA-1 Vega RP-1
Vega RP-1 Destination Display Boards
Destination Display Boards Vega BLE module
Vega BLE module Vega MT-5
Vega MT-5 ESCD
ESCD 


